ANY OpenSees from a Notebook#
Running OpenSees & OpenSeesPy Input Scripts from a DesignSafe Jupyter Notebook
by Silvia Mazzoni, DesignSafe, 2025
This notebook shows how to run any OpenSees script — whether written in Tcl or Python (OpenSeesPy) — using Python’s built-in os library to execute commands just like in a terminal.
You can apply this technique in:
A Jupyter notebook, for an interactive and user-friendly experience
A standalone Python script, for automated or large-scale workflows
Why Use This Approach?#
It makes running OpenSees in the DesignSafe JupyterHub environment highly user-friendly
It lets you build seamless, Python-driven workflows that can include preprocessing, simulation, and postprocessing in one place
It works with any version of OpenSees already available in the Jupyter environment
You can also apply the same method to call OpenSees on an HPC system (e.g., Stampede3), making it easier to scale up or integrate into continuous workflows
Key Concepts:#
Use
os.system()to call.tclor.pyinput files from PythonOutputs go to the path defined in your script
%run(notebook magic) is more limited — it doesn’t accept arguments — soos.system()offers greater flexibility
Using local utilities library
cwd = os.getcwd()
print('current directory:',cwd)
current directory: /home/jupyter/MyData/_ToCommunityData/OpenSees/TrainingMaterial/training-OpenSees-on-DesignSafe/Jupyter_Notebooks
Define Base Path of Input Files.#
OpsScriptsPath = os.path.abspath('../Examples_OpenSees/BasicExamples')
print('OpsScriptsPath:',OpsScriptsPath)
OpsScriptsPath: /home/jupyter/MyData/_ToCommunityData/OpenSees/TrainingMaterial/training-OpenSees-on-DesignSafe/Examples_OpenSees/BasicExamples
Move to user’s home directory#
This way you can save files to your home path – you can’t write to CommunityData
os.chdir(os.path.expanduser('~')) # ~ the tilda is a shortcut to the uers's home path.
cwd = os.getcwd()
print('current directory:',cwd)
current directory: /home/jupyter
Create a temporary directory for our data and move to it#
We want the directory to be within MyData.
tmpDir = 'MyData/tmp_training'
os.makedirs(tmpDir, exist_ok=True)
os.chdir(tmpDir)
cwd = os.getcwd()
print('new current directory:',cwd)
new current directory: /home/jupyter/MyData/tmp_training
# !pip install OpenSeesPy (if needed)
Sequential#
TCL#
OpenSees.exe sequential#
inputFile = 'Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.tcl'
Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.tcl
# /home/jupyter/MyData/_ToCommunityData/OpenSees/TrainingMaterial/training-OpenSees-on-DesignSafe/Examples_OpenSees/BasicExamples/Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.tcl
# OpenSees Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.tcl
############################################################
# EXAMPLE:
# Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.tcl
# for OpenSees.exe (tcl)
# --------------------------------------------------------#
# by: Silvia Mazzoni, 2020
# silviamazzoni@yahoo.com
############################################################
# This file was obtained by updating the Tcl script in the original examples manual
# You can find the original Examples:
# https://opensees.berkeley.edu/wiki/index.php/Examples_Manual
# Original Examples by By Silvia Mazzoni & Frank McKenna, 2006, in Tcl
############################################################
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Example 1. cantilever 2D
# static pushover analysis with gravity.
# all units are in kip, inch, second
# elasticBeamColumn ELEMENT
# Silvia Mazzoni & Frank McKenna, 2006
#
# ^Y
# |
# 2 __
# | |
# | |
# | |
# (1) 36'
# | |
# | |
# | |
# =1= ---- -------->X
#
#
if {[llength $argv]>0} {
puts "Command-Line Arguments (argv): $argv"
}
set LcolList "100 120 200 240 300 360 400 480"
# ----------------------------------------------
set dataDir DataTCL; # set up name of data directory
file mkdir $dataDir; # create data directory
set count 0;
foreach Lcol $LcolList {
# SET UP ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
wipe; # clear opensees model
model basic -ndm 2 -ndf 3; # 2 dimensions, 3 dof per node
# define GEOMETRY -------------------------------------------------------------
# nodal coordinates:
node 1 0 0; # node#, X Y
node 2 0 $Lcol
# Single point constraints -- Boundary Conditions
fix 1 1 1 1; # node DX DY RZ
# nodal masses:
mass 2 5.18 0. 0.; # node#, Mx My Mz, Mass=Weight/g.
# Define ELEMENTS -------------------------------------------------------------
# define geometric transformation: performs a linear geometric transformation of beam stiffness
# and resisting force from the basic system to the global-coordinate system
geomTransf Linear 1; # associate a tag to transformation
# connectivity: (make A very large, 10e6 times its actual value)
element elasticBeamColumn 1 1 2 3600000000 4227 1080000 1;
# Define RECORDERS -------------------------------------------------------------
recorder Node -file ${dataDir}/DFree_Lcol${Lcol}.out -time -node 2 -dof 1 2 3 disp; # displacements of free nodes
recorder Node -file ${dataDir}/DBase_Lcol${Lcol}.out -time -node 1 -dof 1 2 3 disp; # displacements of support nodes
recorder Node -file ${dataDir}/RBase_Lcol${Lcol}.out -time -node 1 -dof 1 2 3 reaction; # support reaction
recorder Element -file ${dataDir}/FCol_Lcol${Lcol}.out -time -ele 1 globalForce; # element forces -- column
recorder Element -file ${dataDir}/DCol_Lcol${Lcol}.out -time -ele 1 deformation; # element deformations -- column
# define GRAVITY -------------------------------------------------------------
timeSeries Linear 1;
pattern Plain 1 1 {
load 2 0. -2000. 0.; # node#, FX FY MZ -- superstructure-weight
}
constraints Plain; # how it handles boundary conditions
numberer Plain; # renumber dof's to minimize band-width (optimization), if you want to
system BandGeneral; # how to store and solve the system of equations in the analysis
test NormDispIncr 1.0e-8 6 ; # determine if convergence has been achieved at the end of an iteration step
algorithm Newton; # use Newton's solution algorithm: updates tangent stiffness at every iteration
integrator LoadControl 0.1; # determine the next time step for an analysis, # apply gravity in 10 steps
analysis Static # define type of analysis static or transient
analyze 10; # perform gravity analysis
loadConst -time 0.0; # hold gravity constant and restart time
# define LATERAL load -------------------------------------------------------------
timeSeries Linear 2;
pattern Plain 2 2 {
load 2 2000. 0.0 0.0; # node#, FX FY MZ -- representative lateral load at top node
}
# pushover: diplacement controlled static analysis
integrator DisplacementControl 2 1 0.1; # switch to displacement control, for node 11, dof 1, 0.1 increment
analyze 1000; # apply 100 steps of pushover analysis to a displacement of 10
puts "Analysis-${count} execution done"
incr count 1;
}
puts "ALL DONE!!!"
os.system(f'OpenSees {OpsScriptsPath}/{inputFile}')
OpenSees -- Open System For Earthquake Engineering Simulation
Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center
Version 3.7.1 64-Bit
(c) Copyright 1999-2016 The Regents of the University of California
All Rights Reserved
(Copyright and Disclaimer @ http://www.berkeley.edu/OpenSees/copyright.html)
Analysis-0 execution done
Analysis-1 execution done
Analysis-2 execution done
Analysis-3 execution done
Analysis-4 execution done
Analysis-5 execution done
Analysis-6 execution done
Analysis-7 execution done
ALL DONE!!!
0
Python#
OpenSeesPy sequential#
inputFile = 'Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py'
Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py
# /home/jupyter/MyData/_ToCommunityData/OpenSees/TrainingMaterial/training-OpenSees-on-DesignSafe/Examples_OpenSees/BasicExamples/Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py
# python Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py
############################################################
# EXAMPLE:
# Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py
# for OpenSeesPy
# --------------------------------------------------------#
# by: Silvia Mazzoni, 2020
# silviamazzoni@yahoo.com
############################################################
# This file was obtained from a conversion of the updated Tcl script
# You can find the original Examples:
# https://opensees.berkeley.edu/wiki/index.php/Examples_Manual
# Original Examples by By Silvia Mazzoni & Frank McKenna, 2006, in Tcl
# Converted to OpenSeesPy by SilviaMazzoni, 2020
############################################################
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Example 1. cantilever 2D
# static pushover analysis with gravity.
# all units are in kip, inch, second
# elasticBeamColumn ELEMENT
# Silvia Mazzoni & Frank McKenna, 2006
#
# ^Y
# |
# 2 __
# | |
# | |
# | |
# (1) 36'
# | |
# | |
# | |
# =1= ---- -------->X
#
#
import openseespy.opensees as ops
import numpy as numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import sys
print(sys.argv)
if len(sys.argv)>1:
print(f'Command-Line Arguments (argv): {sys.argv}')
LColList = [100,120,200,240,300,360,400,480]
#-----------------------------------------
dataDir=f'DataPY'; # set up name of data directory
os.makedirs(dataDir, exist_ok=True); # create data directory
count = 0;
for Lcol in LColList:
ops.wipe()
# SET UP ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ops.wipe() # clear opensees model
ops.model('basic','-ndm',2,'-ndf',3) # 2 dimensions, 3 dof per node
# define GEOMETRY -------------------------------------------------------------
# nodal coordinates:
ops.node(1,0,0) # node , X Y
ops.node(2,0,Lcol)
# Single point constraints -- Boundary Conditions
ops.fix(1,1,1,1) # node DX DY RZ
# nodal masses:
ops.mass(2,5.18,0.,0.) # node , Mx My Mz, Mass=Weight/g.
# Define ELEMENTS -------------------------------------------------------------
# define geometric transformation: performs a linear geometric transformation of beam stiffness
# and resisting force from the basic system to the global-coordinate system
ops.geomTransf('Linear',1) # associate a tag to transformation
# element elasticBeamColumn eleTag iNode jNode A E Iz transfTag
ops.element('elasticBeamColumn',1,1,2,3600000000,4227,1080000,1)
# Define RECORDERS -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/DFree_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',2,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of free nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/DBase_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',1,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of support nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/RBase_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',1,'-dof',1,2,3,'reaction') # support reaction
ops.recorder('Element','-file',f'{dataDir}/FCol_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-ele',1,'globalForce') # element forces -- column
ops.recorder('Element','-file',f'{dataDir}/DCol_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-ele',1,'deformation') # element deformations -- column
# define GRAVITY -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.timeSeries('Linear',1) # timeSeries Linear 1;
ops.pattern('Plain',1,1) #
ops.load(2,0.,-2000.,0.) # node , FX FY MZ -- superstructure-weight
ops.wipeAnalysis() # adding this to clear Analysis module
ops.constraints('Plain') # how it handles boundary conditions
ops.numberer('Plain') # renumber dofs to minimize band-width (optimization), if you want to
ops.system('BandGeneral') # how to store and solve the system of equations in the analysis
ops.test('NormDispIncr',1.0e-8,6) # determine if convergence has been achieved at the end of an iteration step
ops.algorithm('Newton') # use Newtons solution algorithm: updates tangent stiffness at every iteration
ops.integrator('LoadControl',0.1) # determine the next time step for an analysis, apply gravity in 10 steps
ops.analysis('Static') # define type of analysis static or transient
ops.analyze(10) # perform gravity analysis
ops.loadConst('-time',0.0) # hold gravity constant and restart time
# define LATERAL load -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.timeSeries('Linear',2) # timeSeries Linear 2;
ops.pattern('Plain',2,2) #
ops.load(2,2000.,0.0,0.0) # node , FX FY MZ -- representative lateral load at top node
# pushover: diplacement controlled static analysis
ops.integrator('DisplacementControl',2,1,0.1) # switch to displacement control, for node 11, dof 1, 0.1 increment
ops.analyze(1000) # apply 100 steps of pushover analysis to a displacement of 10
print(f'Analysis-{count} execution done')
count +=1
print(f"ALL DONE!!!")
os.system(f'python {OpsScriptsPath}/{inputFile}')
['/home/jupyter/MyData/_ToCommunityData/OpenSees/TrainingMaterial/training-OpenSees-on-DesignSafe/Examples_OpenSees/BasicExamples/Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py']
Analysis-0 execution done
Analysis-1 execution done
Analysis-2 execution done
Analysis-3 execution done
Analysis-4 execution done
Analysis-5 execution done
Analysis-6 execution done
Analysis-7 execution done
ALL DONE!!!
Process 0 Terminating
0
Parallel#
np=4 # number of processors
TCL#
OpenSeesMP parallel using mpiexec#
inputFile = 'Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mp.tcl'
Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mp.tcl
# /home/jupyter/MyData/_ToCommunityData/OpenSees/TrainingMaterial/training-OpenSees-on-DesignSafe/Examples_OpenSees/BasicExamples/Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mp.tcl
# mpiexec -np 3 OpenSeesMP Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mp.tcl
############################################################
# EXAMPLE:
# Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.tcl
# for OpenSees.exe (tcl)
# --------------------------------------------------------#
# by: Silvia Mazzoni, 2020
# silviamazzoni@yahoo.com
############################################################
# This file was obtained by updating the Tcl script in the original examples manual
# You can find the original Examples:
# https://opensees.berkeley.edu/wiki/index.php/Examples_Manual
# Original Examples by By Silvia Mazzoni & Frank McKenna, 2006, in Tcl
############################################################
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Example 1. cantilever 2D
# static pushover analysis with gravity.
# all units are in kip, inch, second
# elasticBeamColumn ELEMENT
# Silvia Mazzoni & Frank McKenna, 2006
#
# ^Y
# |
# 2 __
# | |
# | |
# | |
# (1) 36'
# | |
# | |
# | |
# =1= ---- -------->X
#
#
set pid [getPID]
set np [getNP]
puts "pid $pid of np=$np started"
if {[llength $argv]>0} {
puts "pid $pid of np=$np Command-Line Arguments (argv): $argv"
}
set LcolList "100 120 200 240 300 360 400 480"
# ----------------------------------------------
set dataDir DataTCLmp; # set up name of data directory
file mkdir $dataDir; # create data directory
set count 0;
foreach Lcol $LcolList {
# check if count is a multiple of pid : "is it its turn?"
if {[expr $count % $np] == $pid} {
# SET UP ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
wipe; # clear opensees model
model basic -ndm 2 -ndf 3; # 2 dimensions, 3 dof per node
# define GEOMETRY -------------------------------------------------------------
# nodal coordinates:
node 1 0 0; # node#, X Y
node 2 0 $Lcol
# Single point constraints -- Boundary Conditions
fix 1 1 1 1; # node DX DY RZ
# nodal masses:
mass 2 5.18 0. 0.; # node#, Mx My Mz, Mass=Weight/g.
# Define ELEMENTS -------------------------------------------------------------
# define geometric transformation: performs a linear geometric transformation of beam stiffness
# and resisting force from the basic system to the global-coordinate system
geomTransf Linear 1; # associate a tag to transformation
# connectivity: (make A very large, 10e6 times its actual value)
# element elasticBeamColumn $eleTag $iNode $jNode $A $E $Iz $transfTag
element elasticBeamColumn 1 1 2 3600000000 4227 1080000 1;
# Define RECORDERS -------------------------------------------------------------
recorder Node -file ${dataDir}/DFree_Lcol${Lcol}.out -time -node 2 -dof 1 2 3 disp; # displacements of free nodes
recorder Node -file ${dataDir}/DBase_Lcol${Lcol}.out -time -node 1 -dof 1 2 3 disp; # displacements of support nodes
recorder Node -file ${dataDir}/RBase_Lcol${Lcol}.out -time -node 1 -dof 1 2 3 reaction; # support reaction
recorder Element -file ${dataDir}/FCol_Lcol${Lcol}.out -time -ele 1 globalForce; # element forces -- column
recorder Element -file ${dataDir}/DCol_Lcol${Lcol}.out -time -ele 1 deformation; # element deformations -- column
# define GRAVITY -------------------------------------------------------------
timeSeries Linear 1;
pattern Plain 1 1 {
load 2 0. -2000. 0.; # node#, FX FY MZ -- superstructure-weight
}
constraints Plain; # how it handles boundary conditions
numberer Plain; # renumber dof's to minimize band-width (optimization), if you want to
system BandGeneral; # how to store and solve the system of equations in the analysis
test NormDispIncr 1.0e-8 6 ; # determine if convergence has been achieved at the end of an iteration step
algorithm Newton; # use Newton's solution algorithm: updates tangent stiffness at every iteration
integrator LoadControl 0.1; # determine the next time step for an analysis, # apply gravity in 10 steps
analysis Static # define type of analysis static or transient
analyze 10; # perform gravity analysis
loadConst -time 0.0; # hold gravity constant and restart time
# define LATERAL load -------------------------------------------------------------
timeSeries Linear 2;
pattern Plain 2 2 {
load 2 2000. 0.0 0.0; # node#, FX FY MZ -- representative lateral load at top node
}
# pushover: diplacement controlled static analysis
integrator DisplacementControl 2 1 0.1; # switch to displacement control, for node 11, dof 1, 0.1 increment
analyze 1000; # apply 100 steps of pushover analysis to a displacement of 10
puts "pid $pid of $np Analysis-${count} execution done"
}
incr count 1;
}
puts "pid $pid ALL DONE!!!"
os.system(f'mpiexec -np {np} OpenSeesMP {OpsScriptsPath}/{inputFile}')
OpenSees -- Open System For Earthquake Engineering Simulation
Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center
Version 3.7.1 64-Bit
(c) Copyright 1999-2016 The Regents of the University of California
All Rights Reserved
(Copyright and Disclaimer @ http://www.berkeley.edu/OpenSees/copyright.html)
pid 2 of np=4 started
pid 1 of np=4 started
pid 0 of np=4 started
pid 3 of np=4 started
pid 0 of 4 Analysis-0 execution done
pid 2 of 4 Analysis-2 execution done
pid 1 of 4 Analysis-1 execution done
pid 3 of 4 Analysis-3 execution done
pid 0 of 4 Analysis-4 execution done
pid 0 ALL DONE!!!
Process Terminating 0
pid 2 of 4 Analysis-6 execution done
pid 2 ALL DONE!!!
Process Terminating 2
pid 1 of 4 Analysis-5 execution done
pid 1 ALL DONE!!!
Process Terminating 1
pid 3 of 4 Analysis-7 execution done
pid 3 ALL DONE!!!
Process Terminating 3
0
f'mpiexec -np {np} OpenSeesMP {OpsScriptsPath}/{inputFile}'
'mpiexec -np 4 OpenSeesMP /home/jupyter/MyData/_ToCommunityData/OpenSees/TrainingMaterial/training-OpenSees-on-DesignSafe/Examples_OpenSees/BasicExamples/Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mp.tcl'
Python#
OpenSeesPy parallel using mpiexec#
inputFile = 'Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mpi.py'
Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mpi.py
# /home/jupyter/MyData/_ToCommunityData/OpenSees/TrainingMaterial/training-OpenSees-on-DesignSafe/Examples_OpenSees/BasicExamples/Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mpi.py
# mpiexec -np 3 python Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mpi.py
import openseespy.opensees as ops
import numpy as numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import os
ops.start()
pid = ops.getPID()
np = ops.getNP()
print(f'pid {pid} of {np} started')
if len(sys.argv)>1:
print(f'mpi -- python pid {pid} of {np} Command-Line Arguments (argv): {sys.argv}')
LColList = [100,120,200,240,300,360,400,480]
#-----------------------------------------
dataDir=f'DataPYmpi'; # set up name of data directory
os.makedirs(dataDir, exist_ok=True); # create data directory
count = 0;
for Lcol in LColList:
# check if count is a multiple of pid : "is it its turn?"
if count % np == pid:
ops.wipe()
# SET UP ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ops.wipe() # clear opensees model
ops.model('basic','-ndm',2,'-ndf',3) # 2 dimensions, 3 dof per node
# define GEOMETRY -------------------------------------------------------------
# nodal coordinates:
ops.node(1,0,0) # node , X Y
ops.node(2,0,Lcol)
# Single point constraints -- Boundary Conditions
ops.fix(1,1,1,1) # node DX DY RZ
# nodal masses:
ops.mass(2,5.18,0.,0.) # node , Mx My Mz, Mass=Weight/g.
# Define ELEMENTS -------------------------------------------------------------
# define geometric transformation: performs a linear geometric transformation of beam stiffness
# and resisting force from the basic system to the global-coordinate system
ops.geomTransf('Linear',1) # associate a tag to transformation
# element elasticBeamColumn eleTag iNode jNode A E Iz transfTag
ops.element('elasticBeamColumn',1,1,2,3600000000,4227,1080000,1)
# Define RECORDERS -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/DFree_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',2,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of free nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/DBase_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',1,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of support nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/RBase_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',1,'-dof',1,2,3,'reaction') # support reaction
ops.recorder('Element','-file',f'{dataDir}/FCol_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-ele',1,'globalForce') # element forces -- column
ops.recorder('Element','-file',f'{dataDir}/DCol_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-ele',1,'deformation') # element deformations -- column
# define GRAVITY -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.timeSeries('Linear',1) # timeSeries Linear 1;
ops.pattern('Plain',1,1) #
ops.load(2,0.,-2000.,0.) # node , FX FY MZ -- superstructure-weight
ops.wipeAnalysis() # adding this to clear Analysis module
ops.constraints('Plain') # how it handles boundary conditions
ops.numberer('Plain') # renumber dofs to minimize band-width (optimization), if you want to
ops.system('BandGeneral') # how to store and solve the system of equations in the analysis
ops.test('NormDispIncr',1.0e-8,6) # determine if convergence has been achieved at the end of an iteration step
ops.algorithm('Newton') # use Newtons solution algorithm: updates tangent stiffness at every iteration
ops.integrator('LoadControl',0.1) # determine the next time step for an analysis, apply gravity in 10 steps
ops.analysis('Static') # define type of analysis static or transient
ops.analyze(10) # perform gravity analysis
ops.loadConst('-time',0.0) # hold gravity constant and restart time
# define LATERAL load -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.timeSeries('Linear',2) # timeSeries Linear 2;
ops.pattern('Plain',2,2) #
ops.load(2,2000.,0.0,0.0) # node , FX FY MZ -- representative lateral load at top node
# pushover: diplacement controlled static analysis
ops.integrator('DisplacementControl',2,1,0.1) # switch to displacement control, for node 11, dof 1, 0.1 increment
ops.analyze(1000) # apply 100 steps of pushover analysis to a displacement of 10
print(f'pid {pid} of np={np} Analysis-{count} execution done')
count +=1
print(f"pid {pid} of np={np} ALL DONE!!!")
os.system(f'mpiexec -np {np} python {OpsScriptsPath}/{inputFile}')
print('If you only see "pid=0" and "np=1", then the MPI implementation failed!')
pid 0 of 1 started
pid 0 of 1 started
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-0 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-0 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-1 execution done
pid 0 of 1 started
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-1 execution done
pid 0 of 1 started
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-2 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-0 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-0 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-3 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-2 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-1 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-4 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-1 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-3 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-2 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-5 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-4 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-3 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-2 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-6 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-4 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-5 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-3 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-7 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 ALL DONE!!!
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-6 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-5 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-4 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-6 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-7 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 ALL DONE!!!
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-5 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-7 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 ALL DONE!!!
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-6 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 Analysis-7 execution done
pid 0 of np=1 ALL DONE!!!
If you only see "pid=0" and "np=1", then the MPI implementation failed!
Process 0 Terminating
Process 0 Terminating
Process 0 Terminating
Process 0 Terminating
OpenSeesPy parallel using mpi4py#
inputFile = 'Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mpi4py.py'
Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mpi4py.py
# /home/jupyter/MyData/_ToCommunityData/OpenSees/TrainingMaterial/training-OpenSees-on-DesignSafe/Examples_OpenSees/BasicExamples/Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mpi4py.py
# mpiexec -np 3 python Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.mpi4py.py
import openseespy.opensees as ops
import numpy as numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import os
from mpi4py import MPI
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
pid = comm.Get_rank()
np=comm.Get_size()
print(f'mpi4py -- python pid {pid} of {np} started')
if len(sys.argv)>1:
print(f'mpi4py -- python pid {pid} of {np} Command-Line Arguments (argv): {sys.argv}')
LColList = [100,120,200,240,300,360,400,480]
#-----------------------------------------
dataDir=f'DataPYmpi4py'; # set up name of data directory
os.makedirs(dataDir, exist_ok=True); # create data directory
count = 0;
for Lcol in LColList:
# check if count is a multiple of pid : "is it its turn?"
if count % np == pid:
ops.wipe()
# SET UP ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ops.wipe() # clear opensees model
ops.model('basic','-ndm',2,'-ndf',3) # 2 dimensions, 3 dof per node
# define GEOMETRY -------------------------------------------------------------
# nodal coordinates:
ops.node(1,0,0) # node , X Y
ops.node(2,0,Lcol)
# Single point constraints -- Boundary Conditions
ops.fix(1,1,1,1) # node DX DY RZ
# nodal masses:
ops.mass(2,5.18,0.,0.) # node , Mx My Mz, Mass=Weight/g.
# Define ELEMENTS -------------------------------------------------------------
# define geometric transformation: performs a linear geometric transformation of beam stiffness
# and resisting force from the basic system to the global-coordinate system
ops.geomTransf('Linear',1) # associate a tag to transformation
# connectivity: (make A very large, 10e6 times its actual value)
ops.element('elasticBeamColumn',1,1,2,3600000000,4227,1080000,1)
# Define RECORDERS -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/DFree_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',2,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of free nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/DBase_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',1,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of support nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/RBase_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',1,'-dof',1,2,3,'reaction') # support reaction
ops.recorder('Element','-file',f'{dataDir}/FCol_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-ele',1,'globalForce') # element forces -- column
ops.recorder('Element','-file',f'{dataDir}/DCol_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-ele',1,'deformation') # element deformations -- column
# define GRAVITY -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.timeSeries('Linear',1) # timeSeries Linear 1;
ops.pattern('Plain',1,1) #
ops.load(2,0.,-2000.,0.) # node , FX FY MZ -- superstructure-weight
ops.wipeAnalysis() # adding this to clear Analysis module
ops.constraints('Plain') # how it handles boundary conditions
ops.numberer('Plain') # renumber dofs to minimize band-width (optimization), if you want to
ops.system('BandGeneral') # how to store and solve the system of equations in the analysis
ops.test('NormDispIncr',1.0e-8,6) # determine if convergence has been achieved at the end of an iteration step
ops.algorithm('Newton') # use Newtons solution algorithm: updates tangent stiffness at every iteration
ops.integrator('LoadControl',0.1) # determine the next time step for an analysis, apply gravity in 10 steps
ops.analysis('Static') # define type of analysis static or transient
ops.analyze(10) # perform gravity analysis
ops.loadConst('-time',0.0) # hold gravity constant and restart time
# define LATERAL load -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.timeSeries('Linear',2) # timeSeries Linear 2;
ops.pattern('Plain',2,2) #
ops.load(2,2000.,0.0,0.0) # node , FX FY MZ -- representative lateral load at top node
# pushover: diplacement controlled static analysis
ops.integrator('DisplacementControl',2,1,0.1) # switch to displacement control, for node 11, dof 1, 0.1 increment
ops.analyze(1000) # apply 100 steps of pushover analysis to a displacement of 10
print(f'pid {pid} of np={np} Analysis-{count} execution done')
count +=1
print(f"pid {pid} of np={np} ALL DONE!!!")
os.system(f'mpiexec -np {np} python {OpsScriptsPath}/{inputFile}')
mpi4py -- python pid 0 of 4 started
mpi4py -- python pid 1 of 4 started
mpi4py -- python pid 3 of 4 started
mpi4py -- python pid 2 of 4 started
pid 2 of np=4 Analysis-2 execution done
pid 1 of np=4 Analysis-1 execution done
pid 0 of np=4 Analysis-0 execution done
pid 3 of np=4 Analysis-3 execution done
pid 1 of np=4 Analysis-5 execution done
pid 1 of np=4 ALL DONE!!!
pid 0 of np=4 Analysis-4 execution done
pid 0 of np=4 ALL DONE!!!
pid 2 of np=4 Analysis-6 execution done
pid 2 of np=4 ALL DONE!!!
pid 3 of np=4 Analysis-7 execution done
pid 3 of np=4 ALL DONE!!!
Process 0 Terminating
Process 0 Terminating
Process 0 Terminating
Process 0 Terminating
0
Run OpenSeesPy script within this notebook#
running the script in this manner maintains all variable definitions and OpenSees-Model Objects (unless wipe was used)
inputFile = 'Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py'
Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py
# /home/jupyter/MyData/_ToCommunityData/OpenSees/TrainingMaterial/training-OpenSees-on-DesignSafe/Examples_OpenSees/BasicExamples/Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py
# python Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py
############################################################
# EXAMPLE:
# Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py
# for OpenSeesPy
# --------------------------------------------------------#
# by: Silvia Mazzoni, 2020
# silviamazzoni@yahoo.com
############################################################
# This file was obtained from a conversion of the updated Tcl script
# You can find the original Examples:
# https://opensees.berkeley.edu/wiki/index.php/Examples_Manual
# Original Examples by By Silvia Mazzoni & Frank McKenna, 2006, in Tcl
# Converted to OpenSeesPy by SilviaMazzoni, 2020
############################################################
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Example 1. cantilever 2D
# static pushover analysis with gravity.
# all units are in kip, inch, second
# elasticBeamColumn ELEMENT
# Silvia Mazzoni & Frank McKenna, 2006
#
# ^Y
# |
# 2 __
# | |
# | |
# | |
# (1) 36'
# | |
# | |
# | |
# =1= ---- -------->X
#
#
import openseespy.opensees as ops
import numpy as numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import sys
print(sys.argv)
if len(sys.argv)>1:
print(f'Command-Line Arguments (argv): {sys.argv}')
LColList = [100,120,200,240,300,360,400,480]
#-----------------------------------------
dataDir=f'DataPY'; # set up name of data directory
os.makedirs(dataDir, exist_ok=True); # create data directory
count = 0;
for Lcol in LColList:
ops.wipe()
# SET UP ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ops.wipe() # clear opensees model
ops.model('basic','-ndm',2,'-ndf',3) # 2 dimensions, 3 dof per node
# define GEOMETRY -------------------------------------------------------------
# nodal coordinates:
ops.node(1,0,0) # node , X Y
ops.node(2,0,Lcol)
# Single point constraints -- Boundary Conditions
ops.fix(1,1,1,1) # node DX DY RZ
# nodal masses:
ops.mass(2,5.18,0.,0.) # node , Mx My Mz, Mass=Weight/g.
# Define ELEMENTS -------------------------------------------------------------
# define geometric transformation: performs a linear geometric transformation of beam stiffness
# and resisting force from the basic system to the global-coordinate system
ops.geomTransf('Linear',1) # associate a tag to transformation
# element elasticBeamColumn eleTag iNode jNode A E Iz transfTag
ops.element('elasticBeamColumn',1,1,2,3600000000,4227,1080000,1)
# Define RECORDERS -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/DFree_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',2,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of free nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/DBase_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',1,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of support nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file',f'{dataDir}/RBase_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-node',1,'-dof',1,2,3,'reaction') # support reaction
ops.recorder('Element','-file',f'{dataDir}/FCol_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-ele',1,'globalForce') # element forces -- column
ops.recorder('Element','-file',f'{dataDir}/DCol_Lcol{Lcol}.out','-time','-ele',1,'deformation') # element deformations -- column
# define GRAVITY -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.timeSeries('Linear',1) # timeSeries Linear 1;
ops.pattern('Plain',1,1) #
ops.load(2,0.,-2000.,0.) # node , FX FY MZ -- superstructure-weight
ops.wipeAnalysis() # adding this to clear Analysis module
ops.constraints('Plain') # how it handles boundary conditions
ops.numberer('Plain') # renumber dofs to minimize band-width (optimization), if you want to
ops.system('BandGeneral') # how to store and solve the system of equations in the analysis
ops.test('NormDispIncr',1.0e-8,6) # determine if convergence has been achieved at the end of an iteration step
ops.algorithm('Newton') # use Newtons solution algorithm: updates tangent stiffness at every iteration
ops.integrator('LoadControl',0.1) # determine the next time step for an analysis, apply gravity in 10 steps
ops.analysis('Static') # define type of analysis static or transient
ops.analyze(10) # perform gravity analysis
ops.loadConst('-time',0.0) # hold gravity constant and restart time
# define LATERAL load -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.timeSeries('Linear',2) # timeSeries Linear 2;
ops.pattern('Plain',2,2) #
ops.load(2,2000.,0.0,0.0) # node , FX FY MZ -- representative lateral load at top node
# pushover: diplacement controlled static analysis
ops.integrator('DisplacementControl',2,1,0.1) # switch to displacement control, for node 11, dof 1, 0.1 increment
ops.analyze(1000) # apply 100 steps of pushover analysis to a displacement of 10
print(f'Analysis-{count} execution done')
count +=1
print(f"ALL DONE!!!")
exec(open(f'{OpsScriptsPath}/{inputFile}').read())
['/opt/conda/lib/python3.12/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py', '-f', '/home/jupyter/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/kernel-be779e07-1d1b-4a88-93d5-24c6a488f9d5.json']
Command-Line Arguments (argv): ['/opt/conda/lib/python3.12/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py', '-f', '/home/jupyter/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/kernel-be779e07-1d1b-4a88-93d5-24c6a488f9d5.json']
Analysis-0 execution done
Analysis-1 execution done
Analysis-2 execution done
Analysis-3 execution done
Analysis-4 execution done
Analysis-5 execution done
Analysis-6 execution done
Analysis-7 execution done
ALL DONE!!!
Variables & OpenSees model have been preserved:
# OpenSees Model have been preserved (unless wipe has been used)
print('OpenSees Model')
ops.printModel()
OpenSees Model
Current Domain Information
Current Time: 6.19189
Committed Time: 6.19189
NODE DATA: NumNodes: 2
numComponents: 2
Node: 1
Coordinates : 0 0
Disps: 0 0 0
unbalanced Load: 0 0 0
reaction: -12383.8 2000 5.94422e+06
ID : -1 -1 -1
Node: 2
Coordinates : 0 480
Disps: 100 -6.30865e-08 -0.3125
unbalanced Load: 12383.8 -2000 0
reaction: -1.81899e-12 2.27374e-13 -4.65661e-10
Mass :
5.18 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
Rayleigh Factor: alphaM: 0
Rayleigh Forces: 0 0 0
ID : 0 1 2
ELEMENT DATA: NumEle: 1
numComponents: 1
ElasticBeam2d: 1
Connected Nodes: 1 2
CoordTransf: 1
mass density: 0, cMass: 0
release code: 0
End 1 Forces (P V M): 2000 12383.8 5.94422e+06
End 2 Forces (P V M): -2000 -12383.8 -4.65661e-10
SP_Constraints: numConstraints: 3
numComponents: 3
SP_Constraint: 0 Node: 1 DOF: 1 ref value: 0 current value: 0 initial value: 0
SP_Constraint: 1 Node: 1 DOF: 2 ref value: 0 current value: 0 initial value: 0
SP_Constraint: 2 Node: 1 DOF: 3 ref value: 0 current value: 0 initial value: 0
Pressure_Constraints: numConstraints: 0
numComponents: 0
MP_Constraints: numConstraints: 0
numComponents: 0
LOAD PATTERNS: numPatterns: 2
numComponents: 2
Load Pattern: 1
Scale Factor: 1
Linear Series: constant factor: 1
Nodal Loads:
numComponents: 1
Nodal Load: 2 load : 0 -2000 0
Elemental Loads:
numComponents: 0
Single Point Constraints:
numComponents: 0
Load Pattern: 2
Scale Factor: 1
Linear Series: constant factor: 1
Nodal Loads:
numComponents: 1
Nodal Load: 2 load : 2000 0 0
Elemental Loads:
numComponents: 0
Single Point Constraints:
numComponents: 0
PARAMETERS: numParameters: 0
numComponents: 0
Plot analysis results#
for any of the above analyses
#pick any case
dataDir = 'DataTCL'
Lcol = 400
# check paths:
print('relative path:',os.path.expanduser(dataDir))
print('absolute path:',os.path.abspath(dataDir))
print('current directory:',os.getcwd())
relative path: DataTCL
absolute path: /home/jupyter/MyData/tmp_training/DataTCL
current directory: /home/jupyter/MyData/tmp_training
plt.close('all')
fname3 = f'{dataDir}/DFree_Lcol{Lcol}.out'
dataDFree = numpy.loadtxt(fname3)
plt.subplot(211)
plt.title(f'Ex1a.Canti2D {dataDir}')
plt.grid(True)
plt.plot(dataDFree[:,1])
plt.xlabel('Step Number')
plt.ylabel('Free-Node Displacement')
plt.subplot(212)
plt.grid(True)
plt.plot(dataDFree[:,1],dataDFree[:,0])
plt.xlabel('Free-Node Disp.')
plt.ylabel('Pseudo-Time (~Force)')
plt.savefig(f'{dataDir}/Response.jpg')
plt.show()
print(f'plot saved to {dataDir}/Response_Lcol{Lcol}.jpg')
print('End of Run: Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py.ipynb')
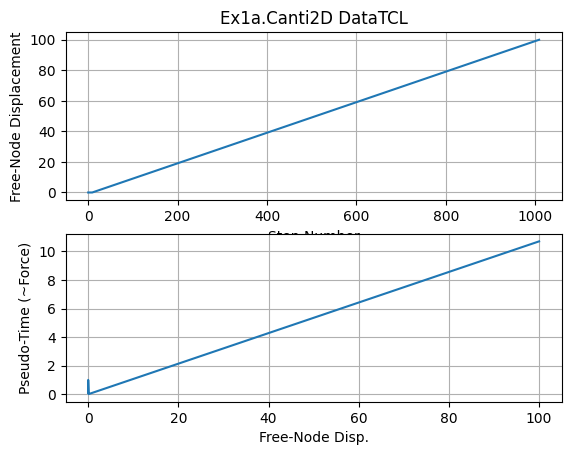
plot saved to DataTCL/Response_Lcol400.jpg
End of Run: Ex1a.Canti2D.Push.py.ipynb
